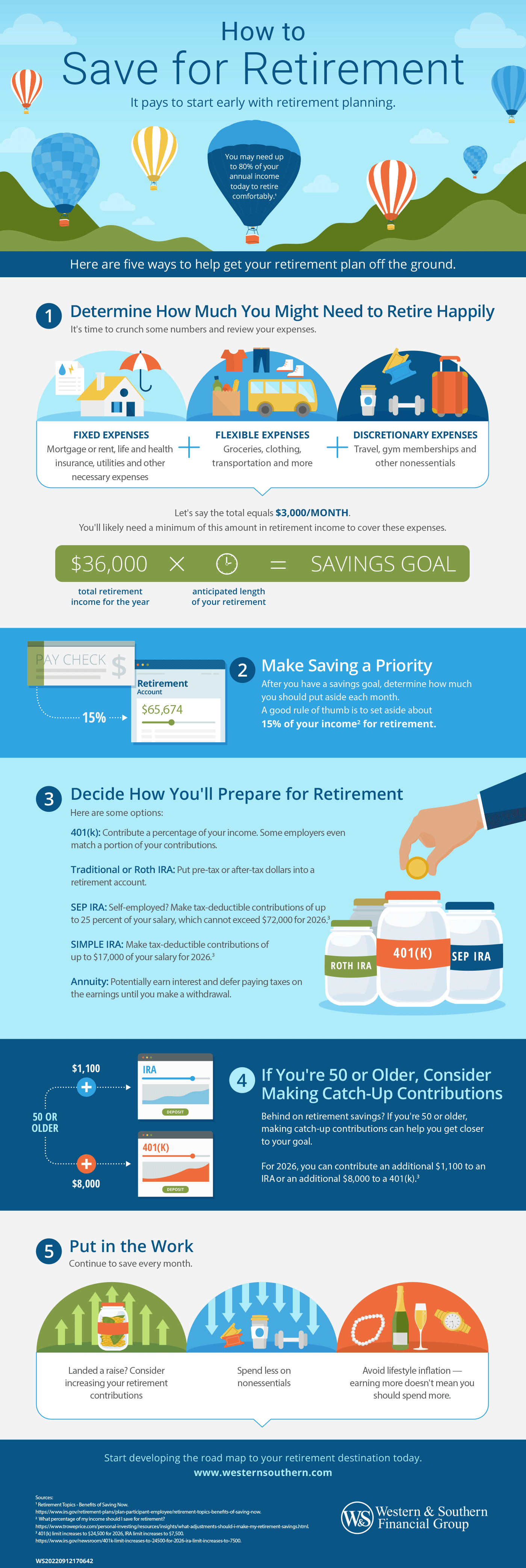


Key Takeaways
- Start by estimating your retirement expenses - including fixed, flexible, and discretionary costs - to calculate how much income you’ll need each month.
- Multiply your estimated annual retirement expenses by your expected years in retirement to set a realistic savings target.
- Aim to save about 15% of your income each month to stay on track toward your retirement goal.
- Consider using retirement accounts such as a 401(k), IRA, SEP IRA, or SIMPLE IRA to maximize tax advantages and potential employer matches.
- If you’re 50 or older, catch-up contributions can help you boost your savings and close any gaps in your retirement plan.
It pays early to start early with retirement planning. You need up to 80% of your annual income today to retire comfortably.1
Here are five ways to help get your retirement plan off the ground.
Step 1: Determine How Much You Might Need to Retire Happily
It's time to crunch some numbers and review your expenses.
- Fixed expenses: Mortgage or rent, life and health insurance, utilities and other necessary expenses
- Flexible expenses: Groceries, clothing, transportation and more
- Discretionary expenses: Travel, gym memberships and other nonessentials
Let's say the total equals $3,000/month. You'll likely need a minimum of this amount in retirement income to cover these expenses.
Multiply your total retirement income for the year by the anticipated length of your retirement to come up with a savings goal.
Step 2: Make Saving a Priority
After you have a savings goal, determine how much you should put aside each month. A good rule of thumb is to set aside about 15% of your income for retirement.2
Step 3: Decide How You'll Prepare for Retirement
Here are some options:
- 401(k): Contribute a percentage of your income. Some employers even match a portion of your contributions.
- Traditional or Roth IRA: Put pre-tax or after-tax dollars into a retirement account.
- SEP IRA: Self-employed? Make tax-deductible contributions of up to 25% of your salary, which cannot exceed $72,000 for 2026.3
- SIMPLE IRA: Make tax-deductible contributions of up to $17,000 for 2026.3
Step 4: If You're 50 or Older, Consider Making Catch-Up Contributions
Behind on retirement savings? If you're 50 or older, making catch-up contributions can help you get closer to your goal.
For 2026, you can contribute an additional $1,100 to an IRA or an additional $8,000 to a 401(k).3
Step 5: Put in the Work
Continue to save every month.
- Landed a raise? Consider increasing your retirement contributions
- Spend less on nonessentials
- Avoid lifestyle inflation - earning more doesn't mean you should spend more
Start developing the road map to your retirement destination today.
Having a retirement plan in place helps support a fulfilling lifestyle when you stop working. Start Your Free Plan
Sources
- Retirement Topics - Benefits of Saving Now. https://www.irs.gov/retirement-plans/plan-participant-employee/retirement-topics-benefits-of-saving-now.
- What percentage of my income should I save for retirement? https://www.troweprice.com/personal-investing/resources/insights/what-adjustments-should-i-make-my-retirement-savings.html.
- 401(k) limit increases to $24,500 for 2026, IRA limit increases to $7,500. https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/401k-limit-increases-to-24500-for-2026-ira-limit-increases-to-7500.












